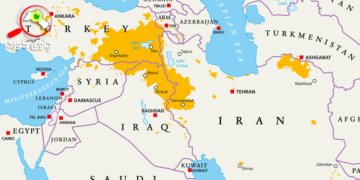
Turkey’s current stance on its relations with Syria has shifted from opposition to the Assad regime and evolved into a more pragmatic approach aimed at normalizing relations. Turkey’s relations with Syria have often been tense over the past decade, especially after the outbreak of the Arab Spring in Syria and the subsequent outbreak of civil war in 2011, which had a profound impact on bilateral relations. Ankara initially sought to overthrow the Damascus government and supported groups that took up arms against Assad. Erdogan described Assad as a “murderer”. The Syrian civil war has sparked a wave of displacement and migration of Syrians inside and outside the country. Turkey has hosted millions of Syrian refugees, leading to the tensest diplomatic relations between the two countries since the 1998 Adana agreement.
Turkey has conducted several military operations in northern Syria to fight ISIS and Kurdish militias such as YPG, which Turkey views as an extension of the PKK, often bringing Turkish forces into direct or indirect conflict with Syrian government forces and their allies. One of the main incidents that exacerbated the tension was the shooting down of a Turkish military plane by Syria in June 2012, which Syria claimed had entered its airspace. Turkey launched Operation Euphrates Shield (2016-2017) under the pretext of clearing ISIS fighters from the Turkish border and preventing Kurdish forces from expanding their territory. The operation was Turkey’s first major offensive in Syria. Turkish military operations continued, such as Operation Olive Grove in 2018 and Operation Peace Spring. In these operations targeted Kurdish-controlled areas in Afrin and along the border, intensifying tensions between Syria and Kurdish groups. Turkey today is looking for a solution to the prolonged conflict and its consequences, such as the massive influx of refugees and increased instability in the region, so Turkey now aims to stabilize its southern border, address security threats and explore economic opportunities in post-war Syria. This change is through engagement with the Assad regime and working with regional and international actors to improve bilateral relations. There are several factors that have affected the relationship between the two countries.
Main causes of tension”
First, security concerns: Turkey’s security concerns stem from several sources, including:
- Kurdish Issue: – Turkey’s growing relations with Bashar al-Assad’s regime are due to security concerns especially regarding the Kurdish issue in northern Syria. In the meantime, Turkey’s main concern is the PKK and its affiliated groups, which currently hold power in West Kurdistan.
- Terrorist groups: Turkey’s interest in normalizing relations with Syria is due to reducing the threat of terrorism originating from Syrian territory, because it has had a direct impact on Turkey’s internal security. Organizations such as ISIS and members of al-Qaeda have established a strong foothold in Syria, which has had an impact on Turkey.
- Refugee crisis: Another motivation for Turkey to normalize relations with Syria is due to the impact of the refugee crisis, which is a complex issue. According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), Turkey hosts the world’s largest number of refugees, with more than 3.6 million Syrian refugees registered.
Methods to normalize relations between Syria and Turkey”
- Diplomatic dialogue initiatives: – Both governments should engage in direct dialogue to address common concerns and establish a framework for normalization, through understanding, diplomatic meetings and confidence building by identifying common interests and the principle of cooperation.
- Identify key issues of conflict: – Key issues between them should be negotiated in order to ensure stability and address security concerns of both countries.
- Reaffirm diplomatic and consular relations: – Re-establish embassies and consulates in each other’s countries.
- Development for economic cooperation: Initiation of trade agreements and economic cooperation for mutual benefit aimed at stability and maintenance of positive relations. This could include joint infrastructure projects and investments.
- Confidence building-: taking steps to reduce tensions and build confidence, such as joint humanitarian projects and their joint efforts in solving the refugee problem. The purpose of these actions is to demonstrate the development and reaffirmation of goodwill and commitment to peaceful and cooperative relations.
- Gaining International Support: – Strengthen relations with global actors to gain support for the normalization process.