Introduction:
Tensions between Russia and Ukraine are considered a long series of geopolitical, cultural and historical conflicts that go back many years, especially after the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 and the division of the Union into several different European nation-states.
In fact, Ukraine’s desire to join NATO to become a permanent member complicated Russian-Ukrainian relations, especially after Ukraine agreed to join NATO in 2008 at a Bucharest summit with members to become a permanent member. However, Russian diplomatic and mediation efforts have continued to try to dissuade Ukraine from becoming a member of NATO because its membership in the alliance would endanger Russia’s security and national interests while Russia shares a border with Ukraine.
After Russia was frustrated by a series of diplomatic and political efforts, tensions escalated until in 2014 Russia annexed Crimea, which was part of Ukraine. This led to continued violence, turmoil and instability in eastern Ukraine. Although Russia’s move was strongly condemned by the international community, Ukraine reacted strongly to the aggression by reaffirming its insistence on membership in the alliance. In 2017, the Ukrainian parliament unanimously adopted the NATO membership law as a fundamental and strategic decision in foreign policy. Russia finally launched a military invasion of Ukraine in 2022, killing hundreds of civilians and causing casualties.
It is interesting to note that although this incident occurred in the territory of two different countries, but had a negative impact on relations between the two countries It also had a negative impact on relations between states and regional forces, changing the international system and creating multilateralism between forces and alliances.
Indeed, the war between Russia and Ukraine can have important consequences for the Middle East, especially for regional forces and their supporters, which can be interpreted differently.
First, the importance of the term geopolitics and the Middle East:
Geopolitics is a compound word consisting of two words, “geo” meaning land, and the word politics meaning “politics”, both of which together mean political geography and geo-politics It was first introduced by the British historian Rudolf Klein in 1916 and then by the German General Karl Haushofer the principles of the theory were formulated and developed.
Geopolitics is the study of the state from the political perspective as a variable concept of the state, that is, not only look at the state from one perspective and evaluate it, but also pays attention to other materials. Oil, gas and other minerals that influence the country’s foreign, economic and military policy strategy, and has the ability to determine the level of foreign policy power to act within the framework of its interests with other countries, whether regionally or internationally.
In fact, the Middle East is considered a strategically important geopolitical region because of the presence of several regional powers in the region, each of which has energy resources such as oil, gas and other underground minerals They have a significant influence in foreign and international policy, including Turkey, Iran, Israel, the Gulf countries, most importantly Saudi Arabia.
There are some key factors of geopolitical importance in the Middle East:
- Energy sources: The Middle East is the world’s largest source of oil and natural gas, an important region for global energy security. region, such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq and the United Arab Emirates, play a major role in global energy markets and have a significant impact on energy prices and energy supply.
- Geopolitical importance: The Middle East, as an important route between Europe, Asia and Africa, crossed a strategic boundary for trade and transportation routes. At the crossroads, the main land and sea areas will provide a unified region hand to provide a unified region and one world’s access to key markets and resources.
- Cultural and religious importance: The Middle East is the birthplace of the world’s great religions, including Islam and Christianity. The ranking and division of religious groups such as Shiites and Sunnis has played a role in the political dynamics and conflict in the region.
- Regional power dynamics: The Middle East is the establishment of several powerful and influential states, such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, Turkey, which compete for power and influence in the process. These countries are often engaged in regional power struggles and alliances that shape the geopolitical dynamics of the Middle East.
Second, the impact of the Russian-Ukrainian war on changing diplomatic relations and geopolitical position of regional forces:
- Saudi Arabia
- The impact of the war and changing energy dynamics in the world economic market:
Demand for Saudi oil has raised since the Russian-Ukrainian war, after the West and the European Union banned Russian oil and natural gas exports to European countries. Saudi Arabia has made a huge profit from the war after deciding to cut oil production in November 2022 in coordination with OPEC, cutting the amount to 1 million barrels per day, pushing the price of Brent crude to $ 90 a barrel. This made it easier for Russia to export its oil and natural gas to India and China as an alternative to exporting it to the European Union.
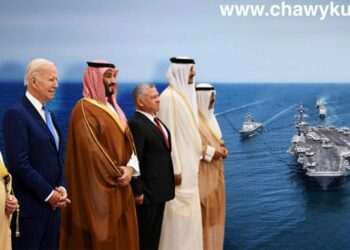
- Saudi Arabia’s diplomatic relations with the United States and Russia
Saudi Arabia plays an important role in determining the level of diplomatic relations with Russia because both countries are considered two important investment and oil export powers. Together, they have made several attempts to stabilize oil prices through agreements within and outside OPEC. Although Saudi Arabia is considered an important ally of the West for 80 years, it has always tried to balance its relations with each of these world powers to work within its interests. But after the Russian-Ukrainian war, Biden called for talks with Saudi King Mohammed bin Salman to coordinate increased oil production to lower oil prices so that Russia fails to provide weapons and ammunition on the battlefield against Ukraine. But Saudi Arabia, contrary to its interests with the United States under OPEC, began to cut oil investment, prompting Russia to sell more oil to China and India after European countries closed their doors to Russia. The United States has since restricted diplomatic relations and arms sales to Saudi Arabia, but has also cut aid to the Yemeni government and refused to put the Houthis on the terror list.
Although Saudi Arabia is considered an important ally of the West for 80 years, it has always tried to balance its relations with each of these world powers to work within its interests. But after the Russian-Ukrainian war, Biden called for talks with Saudi King Mohammed bin Salman to coordinate increased oil production to lower oil prices so that Russia fails to provide weapons and ammunition on the battlefield against Ukraine. But Saudi Arabia, contrary to its interests with the United States under OPEC, began to cut oil investment, prompting Russia to sell more oil to China and India after European countries closed their doors to Russia. The United States has since restricted diplomatic relations and arms sales to Saudi Arabia, but has also cut aid to the Yemeni government and refused to put the Houthis on the terror list.
- Iran
- Iran’s diplomatic relations with Russia and the United States:
Bilateral relations between Iran and Russia are considered to be deep and long-standing. Diplomatic and economic ties continue even after the Ukraine war, with Iran stepping up efforts to sell weapons to Russia. Iran continues to sell oil to Russia in response to a series of disappointments in signing several alliances with the United States to ease Western economic sanctions. Like the failed 2015 nuclear deal signed by former US President Donald Trump, called the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA). The inability of European and American countries to develop political and diplomatic relations with Iran has led Russia to rely on financial and military assistance from Iran. In fact, Russia views Ukraine as a proxy state that the European Union and the United States are using against Russia, which further encourages Russia to use Iran as a tool of revenge against the United States.
- Russia-Iran Economic and Energy Cooperation:
Russia and Iran have acted as two major energy exporters. Russia has begun using Iran as a hub for storage and transportation of oil to Asian markets such as China and India. Trade between the two countries has increased by 20%, estimated at 5 billion dinars. Russia will become Iran’s largest foreign investor after In July 2022, Russia began signing an agreement with the National Iranian Oil Company (NIOC) to provide $40 billion in financial assistance to Iran to invest in its energy sector, including Iran’s oil and gas fields and pipeline construction Russia is a leader in this field and can be a major helper to Iran in this regard, in return, Iran will sell drone models to Russia to help the Russian military, sources show that by the end of February 2022 about 4,600 Iranian-designed drones They were directed at Ukraine and used by Russia.
- Iran’s support for proxy groups and its impact on changing its geopolitical position in the Middle East:
The Iranian government supports an extensive network of proxy forces in the Middle East, such as Hezbollah in Lebanon, the Houthis in Yemen, Hamas in Gaza, and other militia groups in Iraq and Syria The middle alongside other regional forces such as Saudi Arabia and Israel.
The Russian-Ukrainian war has changed Iran’s geopolitical position. For example, Iranian proxy forces in Syria, although they support the Syrian regime with Russian assistance, on the other hand, the presence of Israeli forces in northern Syria Proxy forces such as Hezbollah, although supporting the Assad regime, are a threat to Israel’s national interests. Therefore, Israel must contact Russia to carry out military air strikes against these Iranian proxy forces, which often aim to disrupt the military route to transport weapons against Israel, thus because of these geopolitical changes, Iran must restructure diplomatic and economic relations with Russia In order to balance their relations within the framework of their interests in Syria.
- Turkey
- Turkey’s role in balancing relations between NATO and Russia:
In fact, Turkey is considered an important ally with a prominent position in NATO, established by the European Union and supported financially and militarily by the United States. Turkey has tried to mediate after the Russian-Ukrainian war. Although Turkey receives wheat and grain from Ukraine to meet its needs, it also relies on Russia for energy fuels such as gas and oil. Turkey previously needed Ukraine as a transit country for gas and natural oil from Russian ports to Turkey It has replaced Ukraine by relying on the Turksterm pipeline, which carries natural gas and oil from Russia via the Black Sea to Turkey. This weakens Ukraine’s role as a transit country for Turkey. In addition, Turkey has direct ethnic ties with Ukraine, for example, the majority of Muslim Tatars living in Crimea are Turkish, so Turkey expressed its support for the Muslim Tatars in the occupation of Crimea and called Russia an occupying country. In addition, Turkey’s NATO membership and EU accession efforts have led Turkey to provide military assistance to Ukraine, so Turkey began to sign a free trade agreement with Ukraine in 2021 within the framework of the Crimea Participation Platform to strengthen joint defense forces with Ukraine Preventing Russian threats.
- Turkey’s dominance of the Mediterranean and Black Sea:
In terms of geopolitics, any country that has control over the seas can influence foreign policy and direct them within its interests because Turkey’s geographical location has helped to control the Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. According to the 1936 Montreux agreements signed between Turkey and the United States, France, Germany, Japan, Belgium and Russia, Turkey has the right to own and control the Black Sea, the Bosporus and the Dardanelles Peace should work in accordance with international law in the agreement so that merchant ships can sail freely in peacetime, but in times of war and conflict between two countries that want to use the strait for war and conflict, Turkey can close the strait to warships Therefore, during the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Turkey decided to close its straits to Russian warships at the request of NATO members and Montrex members, although this was against Russia’s interests, but allowed the warships to return to their base in the Black Sea As mentioned in Article 19 of the Agreement.
- Turkey’s diplomatic imbalance between the United States and Russia on the Syrian issue:
Syria was a platform for Turkey to conduct a series of military operations for its interests in Syria. In fact Turkey supports the Assad regime and Syrian opposition forces working against Kurdish forces such as YPG and PKK in eastern Syria and conducting military operations to achieve autonomy for Syrian and Turkish Kurds. Washington’s support for the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), which Turkey sees as an offshoot of the Kurdistan Workers’ Party (PKK) working against the Assad regime has put Turkish interests at risk. But in 2022 after the outbreak of the Russian-Ukrainian war, Moscow increased its support for Iranian militia forces in Syria because of Turkey’s support for weapons and ammunition to Ukraine. This has worried Turkey between supporting Moscow and Washington in Syria.
- Israel
- Development of Israel’s security strategy to limit Iranian expansionism:
Iran and Israel are considered two fierce historical rivals, whose conflicts have always been a hot topic in the Arab and Western media. Iran does not recognize the Jewish state of Israel and has always tried to undermine Israel’s interests through proxy groups such as Hezbollah in Lebanon, Hamas in Palestine and the Houthis in Yemen It has signed security and trade agreements with Gulf countries, including the Abraham Accord. Israel is considered a close US ally that has worked together against Iran’s nuclear program.
Since the Russia-Ukraine war, Israel has repeatedly tried to mediate between Russia and NATO allies. At the beginning of the war, Israel condemned the Russian invasion of Ukraine, but after the imposition of economic and trade sanctions on Russia by the United States, Israel did not go under the imposition of these sanctions as a neutral country.
After the war, Iran directly provided intensive aid to Russia, which led to increased solidarity between Iran and Russia, which caused Israeli protests because it saw Iran as a threat to its interests in the Middle East, especially in Palestine, Lebanon and Syria.
- Russian-Israeli diplomatic relations and military cooperation in Syria:-
Israel supports Russian and Putin policies within the framework of its strategic interests in Syria. In 2015 Moscow and Israel signed a memorandum of understanding that Russia would coordinate to prevent the deployment of anti-Israeli forces in Syria that pose a threat to Israel Israel does not want Iran to use Syria as a major route for the transportation and storage of weapons and ammunition for Lebanese Hezbollah forces. The two sides agreed to form a joint team to fight Iranian drones within 80 kilometers of its altitude Golan. After the Russia-Ukraine war, Western economic sanctions against Moscow and Israel’s humanitarian aid to Ukraine led to further disappointment in Russia, which tightened economic and diplomatic relations with Iran and even adopted new mechanisms to counter Israel in Syria, for example, according to sources 2022 Russia He no longer fought against Shiite militias that wanted to attack Israeli bases and targets in Syria. He also tried to disrupt civilian air patrols in order to disable Israeli GPS.
Conclusion:
- The Russia-Ukraine war changed the foreign policy of the regional powers in the Middle East based on the fact that the United States is no longer the only world power in the Middle East that can control all aspects of foreign policy.Instead, the international system is moving towards a multipolar system alongside powers such as Russia, the United States and China.Regional forces play an influential role in shaping the Russian-Ukrainian war.
- The neutrality of many regional powers in the war except Iran and did not directly support the imposition of economic sanctions on Russia shows the fact that Russia has an important position in the foreign policy of regional powers. It is also one of the five member that have right of veto that can declare war and ceasefire, thus returning Russia to the stage of world politics, which was previously completely weakened after the 1991 Cold War.
- In fact, US influence in the Middle East has declined after a series of Arab Spring revolutions in 2011, the withdrawal of US forces from northeastern Syria and Afghanistan in 2021, which has led regional forces to no longer see the United States as a reliable force in the Middle East. This was clearly felt after Obama’s disappearance from power and the continued practice of successive administrations of Donald Trump and Joe Biden.