After the propaganda was spread by the oil companies; Central Asia, especially the Caspian Sea region, contains huge reserves of energy resources, especially oil and gas, which coincided with the collapse of the Soviet Union and the creation of a power vacuum in the region, so the conflict in the region intensified. The Caspian Sea region was expected to become an important non-OPEC energy supplier in the next few decades, exporting oil and gas to world markets, especially a large producer of natural gas in the region to export gas to countries outside the Caspian Sea. However, the Caspian Sea countries initially faced three main obstacles: First, they had to create a favorable environment to attract investors, and establish domestic infrastructure to produce and export energy. Second, it was necessary to manage the energy wealth in a way that would lead to long-term economic development. Third, energy development brought the risk of militarization and terrorism in the region, which could pose a serious threat to energy resources and investors in the Caspian Sea countries, especially Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan, in the future.
The Caspian Sea is divided among five countries: Russia, Iran, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan. All five countries on the Caspian Sea signed a new legal agreement in Aktau, Kazakhstan, on the status of the Caspian Sea, which appears to be a major compromise because for years the parties could not agree on the division of the coast Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan, as well as Russia and Iran, are very important that the sea is free from any non-regional forces, no army can be present in the sea. The signing of the agreement is primarily important for Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Azerbaijan because in the past the sea was only related to the former Soviet Union and Iran, but now three other countries have become members.
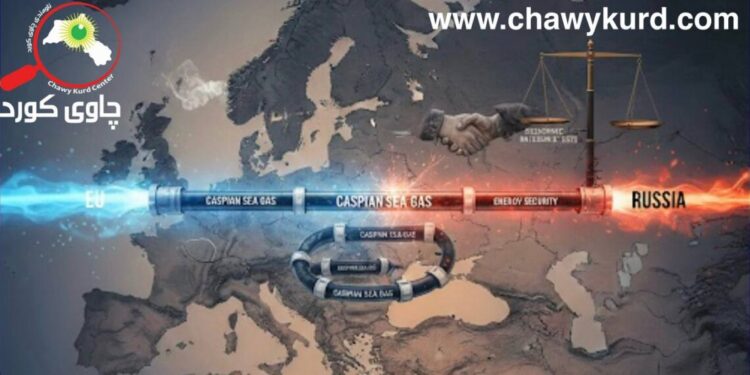
The main points of the agreement are security, economic cooperation, environmental protection, improvement of traffic, etc. Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan have benefited most from the agreement because they have more gas-rich coastlines. “This is a century-old and very important event,” Putin said. “This is the drafting of the Caspian Sea Constitution. In terms of geopolitical relations and energy security, the Caspian Sea plays an important role in relations between the European Union and Central Asia, especially after all five coastal countries signed an agreement on the Caspian Sea in 2018 that offers new prospects for developments in the region. The Caspian Sea contains 25% of the world’s natural gas, which is a large amount for the impact and role on the stability of gas security in the world.
The EU’s policy towards the Caspian Sea region is not under a single foreign policy. From one EU country to another, EU relations with Azerbaijan are shaped by the Eastern Partnership (EAP) as a dimension of the European Neighborhood Policy 2019 follows. The EU’s relations with Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan are part of the EU’s 2019 Central Asia Strategy.
Azerbaijan’s cooperation with the EU, both at the institutional level and with individual countries within the EU, will continue to develop and deepen. Azerbaijan will be an important source of EU energy security both now and in the future, both sides are trying to resolve them, which may not take long, and if most of the problems are resolved before the end of this decade, the EU will be able to rely more and more on Russian gas for access to affordable alternatives.