Executive Summary
This policy analysis examines the impact of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) on the Kurdistan Region, focusing on the opportunities and challenges it presents. The BRI aims to enhance global trade and stimulate economic growth across Asia and beyond through infrastructure investments. For the Kurdistan Region, the BRI offers potential benefits such as improved infrastructure, increased foreign investment, and enhanced trade links. However, it also poses challenges, including economic dependency, political risks, and environmental concerns. This report provides a detailed analysis of these factors and offers policy recommendations to maximize the benefits while mitigating the risks.
Introduction
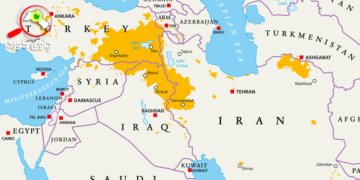
The Belt and Road Initiative, launched by Xi Jinping, President of China in 2013, is a global development strategy aimed at enhancing connectivity and cooperation among nearly 70 countries primarily in Asia, Europe, and Africa. As of 2024, over 150 countries and international organizations have signed cooperation agreements with China under the BRI. The Kurdistan Region, strategically located in the Middle East, stands to gain significantly from this initiative. This report explores the potential impacts of the BRI on the Kurdistan Region, identifying key opportunities and challenges.
Background
The BRI encompasses two main components: the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. It aims to create a vast network of railways, highways, pipelines, and ports, facilitating trade and investment. The Kurdistan Region, with its rich natural resources and strategic location, is an attractive partner for China. However, the region must navigate complex geopolitical dynamics and economic dependencies.
Policy Options
- Enhanced Infrastructure Development: Leverage BRI investments to improve transportation and energy infrastructure.
- Economic Diversification: Use BRI opportunities to diversify the economy beyond oil and gas.
- Strengthened Diplomatic Relations: Foster stronger diplomatic ties with China to ensure mutual benefits.
- Environmental Safeguards: Implement policies to mitigate environmental impacts of BRI projects.
Criteria for Evaluation
– Economic Impact: Assess the potential for economic growth and job creation.
– Political Stability: Evaluate the impact on regional political dynamics.
– Environmental Sustainability: Consider the environmental implications of infrastructure projects.
– Social Benefits: Measure improvements in quality of life and social infrastructure.
Analysis of Policy Options
1. Enhanced Infrastructure Development:
– Pros: Improved connectivity, increased trade, and job creation.
– Cons: Potential for increased debt and economic dependency on China.
2. Economic Diversification:
– Pros: Reduced reliance on oil and gas, fostering sustainable economic growth.
– Cons: Requires significant investment and long-term planning.
3. Strengthened Diplomatic Relations:
– Pros: Enhanced political and economic cooperation, increased foreign investment.
– Cons: Risk of political alignment with China’s strategic interests.
4. Environmental Safeguards:
– Pros: Protection of natural resources and sustainable development.
– Cons: Potential increase in project costs and delays.
Recommendations
- Prioritize Infrastructure Projects: Focus on projects that offer the highest economic returns and strategic value.
- Promote Economic Diversification: Invest in sectors such as agriculture, tourism, and technology.
- Strengthen Diplomatic Engagement: Engage in continuous dialogue with Chinese counterparts to ensure mutual benefits.
- Implement Environmental Regulations: Enforce strict environmental standards for all BRI projects.
Implementation Plan
- Establish a BRI Task Force: Create a dedicated team to oversee BRI projects and ensure alignment with regional priorities.
- Develop a Strategic Investment Plan: Identify and prioritize key infrastructure projects.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve local communities, businesses, and environmental groups in the planning process.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Implement a robust monitoring and evaluation framework to track progress and address challenges.
Conclusion
The Belt and Road Initiative presents significant opportunities for the Kurdistan Region, but it also comes with challenges that must be carefully managed. By adopting a strategic approach that prioritizes infrastructure development, economic diversification, and environmental sustainability, the Kurdistan Region can maximize the benefits of the BRI while mitigating potential risks.
References
- International Institute for Strategic Studies. “China’s Belt and Road Initiative: A Geopolitical and Geo-economic Assessment.” Accessed December 10, 2024. [IISS](https://www.iiss.org/publications/strategic-dossiers/chinas-belt-and-road-initiative/).
- Wolff, Peter. “China’s ‘Belt and Road’ Initiative – Challenges and Opportunities.” German Development Institute, 2016. [DIE](https://www.idos-research.de/uploads/media/Belt_and_Road_V1.pdf).
- Institute of Policy Research. “Belt and Road Initiative: Objectives and Challenges.” Accessed December 10, 2024. [IPRI](https://ipripak.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Paper-BRI-March-2024.pdf).